
Decongestants (usually oxymetazoline 0.05, 2 sprays each nostril twice a day for 3 to 5 days or pseudoephedrine 30 to 60 mg orally 2 to 4 times a day up to a maximum of 240 mg/day for 3 to 5 days) can help open occluded chambers. Diving medicine: a review of current evidence. Treatment with medications for sinus and middle ear barotrauma is identical. SOURCE: Reproduced, with permission, from Lynch JH, Bove AA. Numbness, dizziness, weakness, gait abnormality, hypoesthesia Book overview 1.Sinus barotrauma with acute pain over the sinus area or nasal or postnasal bleeding 2.Middle ear Barotrauma with pain in the ear, bleeding. Significant time at depth 50% develop symptoms within 1 h of surfacing, 90% within 6 h Poorly localized joint pain, rash, itching Immediately upon surfacing or during ascentġ00% oxygen, supportive care, U.S. Stupor, coma, focal weakness, visual disturbances Slow equalization on descent decongestants Slow equalization on descent decongestants, consider antibiotics for tympanic membrane perforationĪcute vertigo, nausea, vomiting, hearing lossīed rest, elevated head, avoidance of Valsalva, otolaryngology consult
read more ).Table 90.2 Summary of Diving-Related ConditionsĪcute ear pain, vertigo, tympanic membrane rupture It can affect the ear (causing ear pain, hearing loss, and/or vestibular symptoms) or the sinuses. Overpressurization in the sphenoid sinus occasionally compresses the optic nerve, causing decreased vision or blindness ( 3, 4 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. Medical and surgical treatment in divers with chronic rhinosinusitis. Maxillary sinus overpressurization can compress the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve, causing hyperesthesia over the cheek. Sinus barotrauma while diving is considered to be the consequence of insufficient paranasal sinus ventilation during ambient pressure changes, when either ascending or descending on a dive, or when diving in a multilevel environment. Pain can be severe, sometimes accompanied by facial tenderness on palpation. Divers experience mild pressure to severe pain, with a feeling of congestion in the involved sinus compartments during ascent or descent and sometimes epistaxis. Sinus barotrauma most often affects the frontal sinuses, followed by the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses ( 3 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. Weakness of both upper and lower face distinguishes facial baroparesis from stroke or arterial gas embolism ( 1 General references Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume.

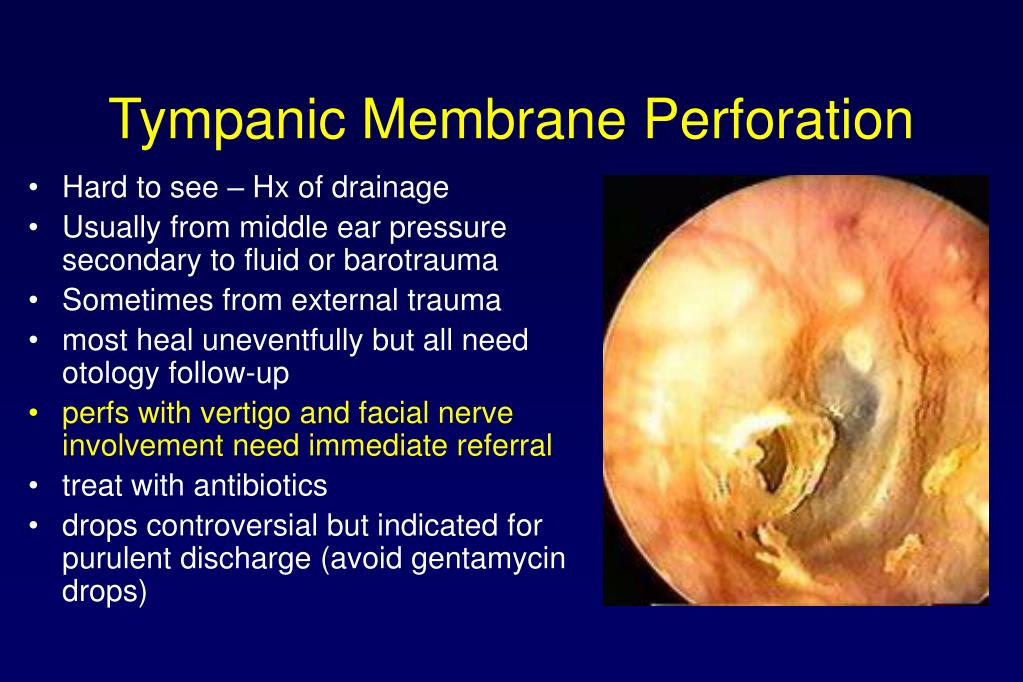
When pressure within the middle ear remains elevated during or after ascent from a dive, the facial nerve can be compressed (facial baroparesis), resulting in ipsilateral upper and lower facial paresis. Barosinusitis, or sinus barotrauma, is a condition that describes the varying degrees of sinonasal injury and/or inflammation that result when the aerated spaces of the nose and sinuses are exposed to an uncompensated change in ambient pressure. On examination of the ear canal, the tympanic membrane may show congestion, hemotympanum, perforation, or lack of mobility during air insufflation with a pneumatic otoscope conductive hearing loss is usually present. Inflow of cold water to the middle ear may result in vertigo, nausea, and disorientation while submerged. Typically, divers experience ear fullness and pain during descent if pressure is not quickly equilibrated, middle ear hemorrhage or tympanic membrane rupture may occur. Diving can affect the external, middle, and inner ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
